Object Oriented Programming Through Java
Master the principles of OOP with Java programming language
About The Subject
Learn the fundamentals of Object-Oriented Programming
Overview
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm that organizes software design around objects — real-world entities that have attributes (data) and behaviors (methods). Java is one of the most popular languages that fully supports OOP concepts, making it powerful, flexible, and easy to maintain.
Class and Object
A class is a blueprint or template, and an object is an instance of that class. Example: Car can be a class, and myCar is an object.
Encapsulation
Wrapping data and code together into a single unit. It protects data using access modifiers like private, public, and protected.
Inheritance
One class can inherit properties and methods from another, promoting code reusability. Example: class Dog extends Animal.
Polymorphism
Allows methods to perform different tasks based on the object calling them — achieved through method overloading and overriding.
Abstraction
Hides implementation details and shows only the essential features — achieved using abstract classes and interfaces.
Platform Independence
Java achieves platform independence through the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), giving it the famous slogan — "Write Once, Run Anywhere."
Faculty Information
Meet your course instructor
Mr. ABDUL SHAHBAAZ KHAN
Assistant Professor
Syllabus
Complete course curriculum and topics


Study Materials
Download notes and reference materials
Click to download the complete OOPS notes (PDF, ~3.0MB)
Lab Details
Practical sessions and schedule
Lab Incharge
Mr. ABDUL SHAHBAAZ KHAN
Lab Schedule
MONDAY - 2:00 PM TO 4:30 PM
Lab Location
Computer Lab - Block A, 2nd Floor


Important Questions & Answers
Previous year questions with detailed solutions
Answer:
Key Features of Java:
Java is a popular, high-level, object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle). It provides several important features that make it powerful and widely used.
1. Simple:
Java is easy to learn and use because it removes complex features like pointers, operator overloading, and multiple inheritance.
2. Object-Oriented:
Everything in Java is treated as an object. It supports OOP concepts such as inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, and abstraction.
3. Platform Independent:
Java code can run on any platform (Windows, Mac, Linux, etc.) without modification, thanks to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
4. Secure:
Java provides a secure environment through features like bytecode verification, sandboxing, and absence of explicit pointers.
5. Robust:
Java handles errors effectively with exception handling and has strong memory management using automatic garbage collection.
6. Multithreaded:
Java allows the execution of multiple threads (lightweight processes) simultaneously, improving performance.
7. Portable:
Java programs are portable because the same .class file can run anywhere a JVM is installed.
8. High Performance (with JIT):
The Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler improves performance by converting bytecode into native machine code at runtime.
Answer:
→ Constructor is like a special method used in object creation & most importantly to initialise non-static properties during the object creation.
→ The name of the constructor would be always similar to class name & it do not contain any return type.
→ We can't create Java program without the constructors. Since compiler automatically adds the constructor if the developer forgets to add it.
Syntax:
[Access Specifier] ClassName(F.A's)
{
// statements
}
Types of Constructors:
→ We have three types of constructors.
1. Default Constructor:
Whenever developer creates a class without constructor, compiler mandatory/compulsarily adds the constructor without formal arguments known as default constructor.
2. Non-Argument Constructor:
If a developer add constructor without formal arguments known as Non-Argument constructor
Ex: A obj = new A();
3. Parameterized Constructor:
A constructor add by developer with formal arguments known as Parameterized constructor which is
mainly used to initialized non static properties during the object creation
Example:
U.L
A obj 1 = new (10,20);
B.P
A(int a, int b){
This.a=a;
This.b=b;
}
Answer:
Inheritance
It is similar to parent & child relationship where non-static properties & behaviour of an parent class/superclass are acquired by sub class object by using extends keyword btw the classes called as Inheritance.
Child class (or) Sub class
A child which acquires another class properties & behaviour is known as sub class /child class.
Parent class (or) super class
A class which provide the property & behaviour to another class is known as parent class/ super class
Only non-static properties & behaviour are inherited to sub class
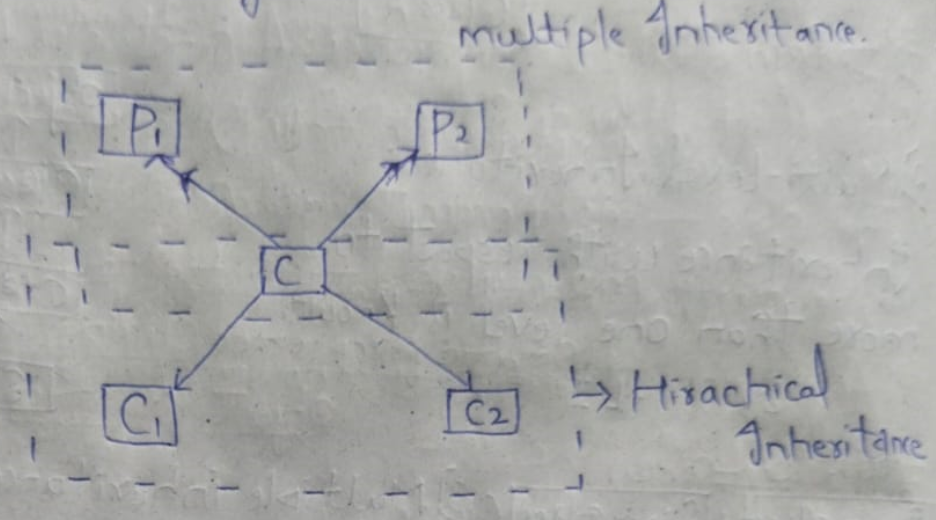
Types of inheritance
There are 5 types of inheritance in java, they are
- Single level inheritance
- Multi-level inheritance
- Multiple inheritance
- Hierarchical inheritance
- Hybrid inheritance
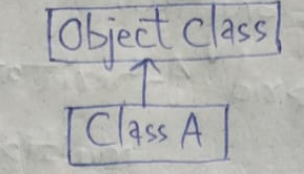
1. Single level inheritance: A subclass inherits from only one superclass.
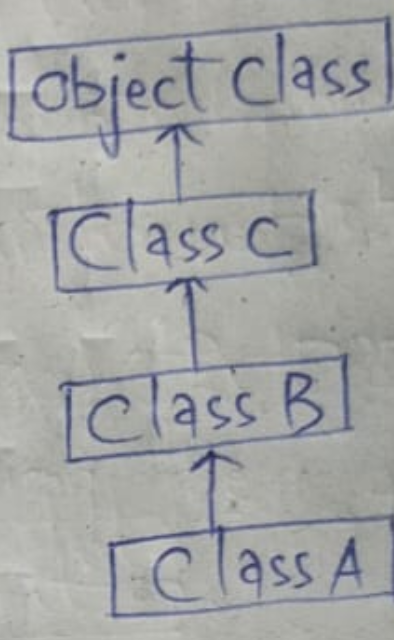
2. Multi-level inheritance:
Inheritance with respect to more than one level is known M-LI
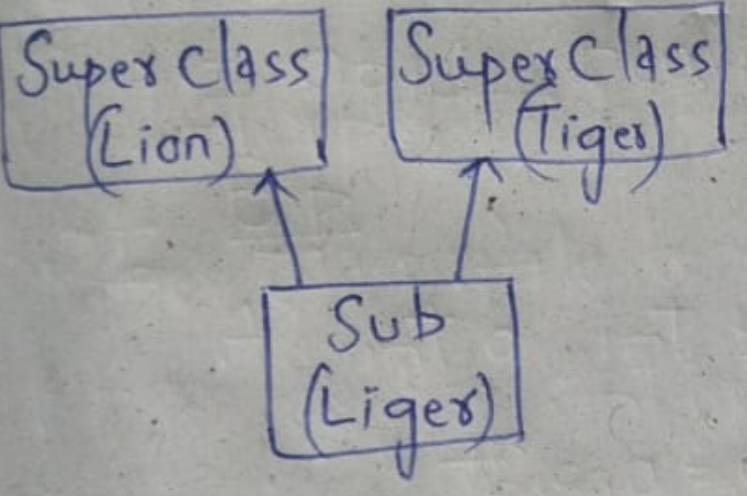
3. Multiple inheritance:
one sub class having multiple super class in a same level is known as m-ln
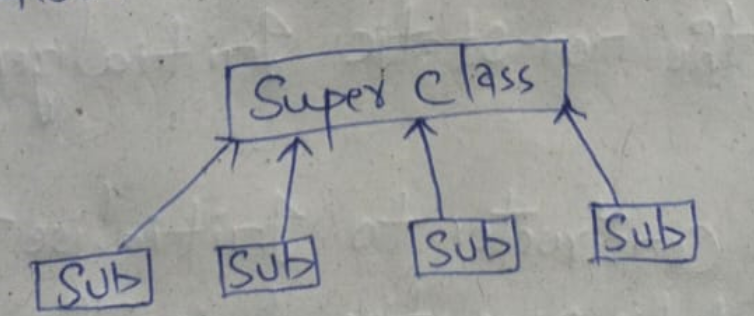
4. Hierarchical inheritance:
one super class having multiple sub class in a same level is known as hierarchical inheritance
5. Hybrid inheritance:
combination of any two types of inheritance is known as hybrid inheritance.
Answer:
In Java, a package is a collection of related classes, interfaces, and sub-packages that are grouped together to avoid name conflicts and to organize files properly. It acts as a namespace that helps to categorize classes logically (like folders in a computer).
Example:
package mypackage;
public class Example {
public void display() {
System.out.println("This is a package example");
}
}
Types of Packages:
1. Built-in Packages (Predefined Packages):
These are packages provided by Java itself.
Answer:
Key Features of Java:
Java is a popular, high-level, object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems (now owned by Oracle). It provides several important features that make it powerful and widely used.
1. Simple:
Java is easy to learn and use because it removes complex features like pointers, operator overloading, and multiple inheritance.
2. Object-Oriented:
Everything in Java is treated as an object. It supports OOP concepts such as inheritance, encapsulation, polymorphism, and abstraction.
3. Platform Independent:
Java code can run on any platform (Windows, Mac, Linux, etc.) without modification, thanks to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
4. Secure:
Java provides a secure environment through features like bytecode verification, sandboxing, and absence of explicit pointers.
5. Robust:
Java handles errors effectively with exception handling and has strong memory management using automatic garbage collection.
6. Multithreaded:
Java allows the execution of multiple threads (lightweight processes) simultaneously, improving performance.
7. Portable:
Java programs are portable because the same .class file can run anywhere a JVM is installed.
8. High Performance (with JIT):
The Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler improves performance by converting bytecode into native machine code at runtime.
ANSWER:
a.The new keyword in java is a crucial operator primarily used for object creation and dynamic memory allocation.It performs several key functions
Example:
Student s=new student();
b.Yes,in java a class can extend multiple interfaces,allowing multiple inheritance of type.
Example:
class demo implements A,B{ }
c.An exeption in java is an unwanted event or error thsat occurs during program execution,distrupting the normal flow of instructions.